 Home Home
 Processors Processors
 Meat Facilities Meat Facilities
 Producers Producers
 Consumers Consumers
 Legislation Legislation
 Market Access Market Access
 News and Events News and Events
 About Us About Us |  | What is a Foodborne Illness?
A foodborne illness is a disease caused by eating foods that has been contaminated by harmful bacteria or other microorganisms.
Pathogens are microorganisms, such as bacteria, virus or fungus that cause disease. Under the right conditions, pathogens grow rapidly, doubling in population every 10 to 30 minutes. Food can become contaminated with pathogens through improper handling, preparation or storage.
Keep in mind, food that contains pathogens or their toxins may look, smell and taste normal.
Which Pathogens Cause Foodborne Illnesses?
The most common foodborne pathogens are:
Campylobacter jejuni,
Clostridium perfringens,
Escherichia coli O157:H7,
Listeria monocytogenes and
Salmonella species.
However, Noroviruses, Hepatitis A and E viruses and mycotoxins and other naturally occurring toxins can also cause foodborne illnesses.
What are the Symptoms?
The most common symptoms include: mild to severe diarrhea, fever, fatigue, nausea, muscle aches, headache, vomiting, and chills. Symptoms can occur hours or even days after eating contaminated food.
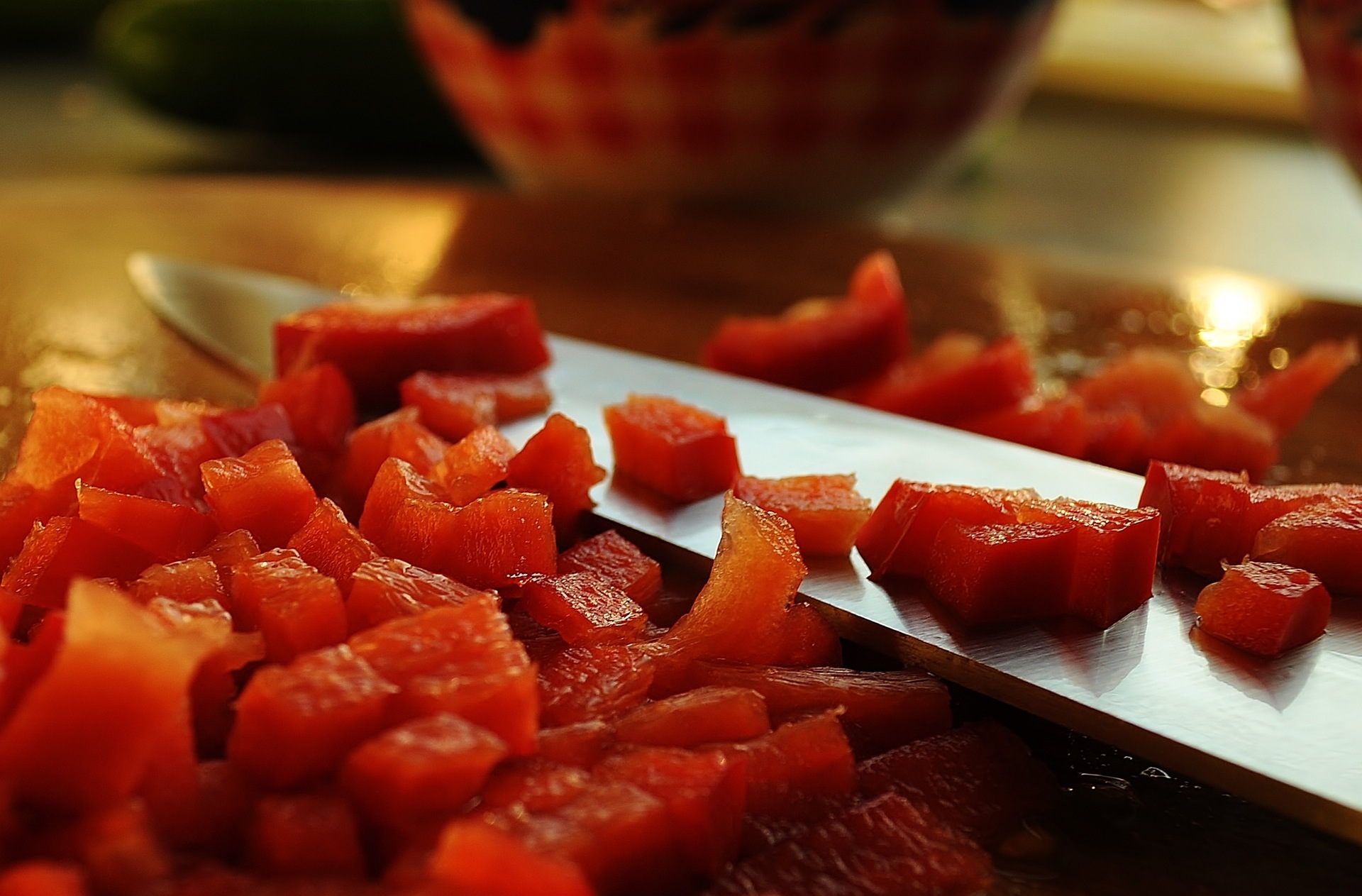
Tips to Avoid Foodborne Illnesses at Home
Note: Don't forget to wash your reusable grocery bags frequently.
| | 
Quick Links
Alberta Health Services
Government of Canada
CFIA
|